The impact of lightning on concrete is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Physical damage: The high temperature and high pressure of lightning may directly damage the surface of concrete, such as cracks, peeling or breaking. This physical damage may weaken the overall strength and stability of the concrete structure.
2. Internal stress: When lightning strikes a concrete building, the strong current will generate induced currents in the steel bars or other metal parts inside the concrete. These induced currents may cause the steel bars to expand due to heat, thereby generating stress inside the concrete. Long-term or multiple lightning strikes may accumulate these stresses and eventually lead to the destruction of the concrete structure.
3. Electromagnetic interference: The strong electromagnetic field generated by lightning may interfere with or damage electronic equipment in concrete buildings. This electromagnetic interference may be transmitted to the inside of the equipment through power lines, signal lines or other metal conductors, affecting its normal operation or causing permanent damage.
4. The impact of lightning protection system: Although concrete buildings are usually equipped with lightning protection systems (such as lightning rods, lightning strips, etc.), lightning may still cause impacts on the lightning protection system itself. For example, a lightning rod may be damaged due to excessive current, or a lightning protection down conductor may be melted due to excessive current. This will weaken the protective effect of the lightning protection system and increase the risk of buildings being directly struck by lightning.
5. Indirect impact: Lightning may also indirectly affect concrete buildings by affecting the surrounding environment. For example, lightning may cause accidents such as fires and explosions, which may cause further damage to concrete buildings. In addition, lightning may also interfere with or damage infrastructure such as power supply systems and communication systems, thereby affecting the normal use of concrete buildings.
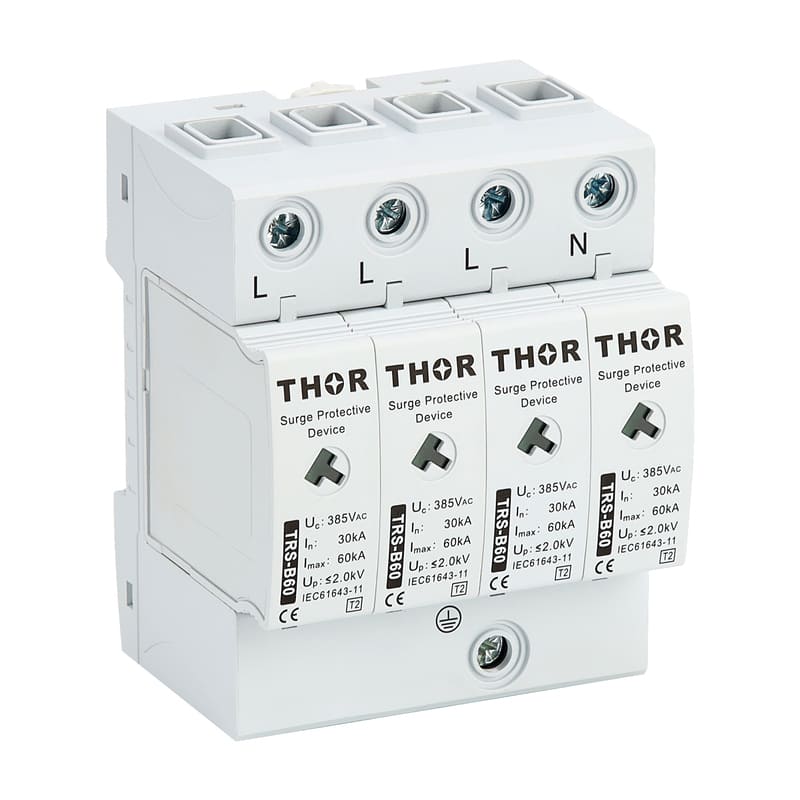
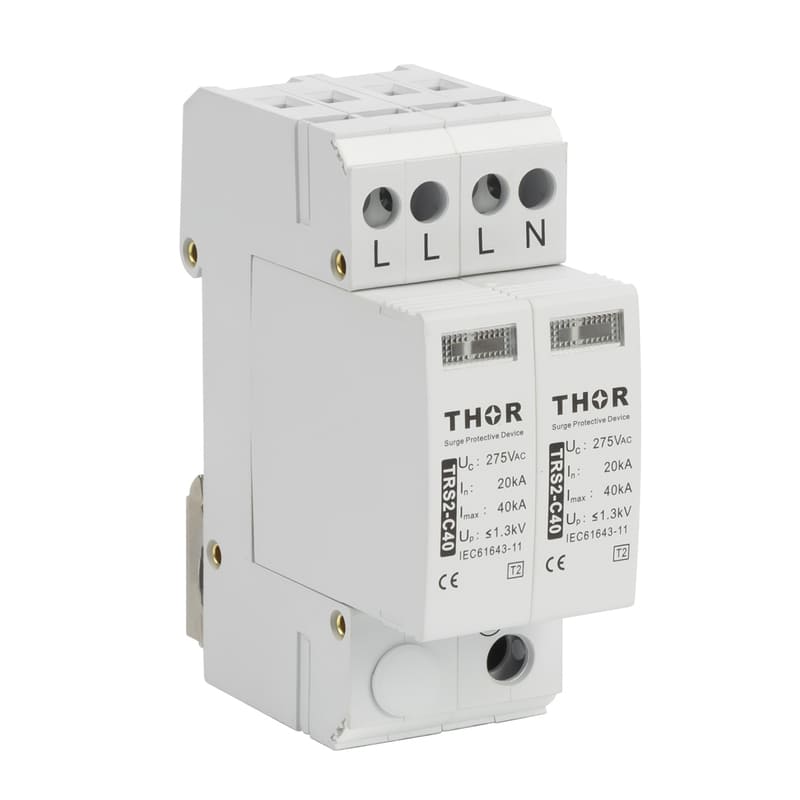
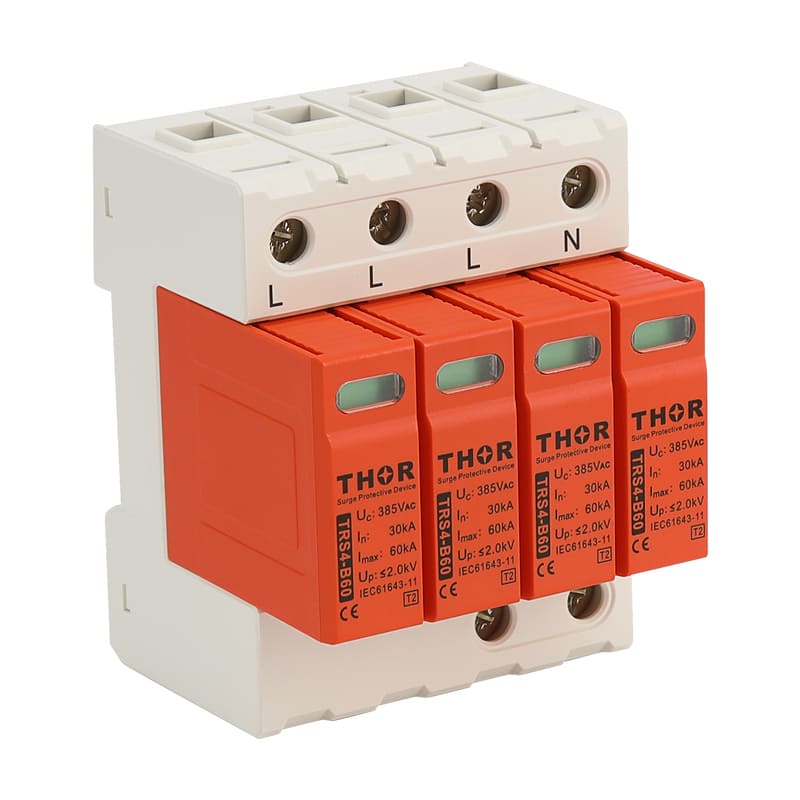
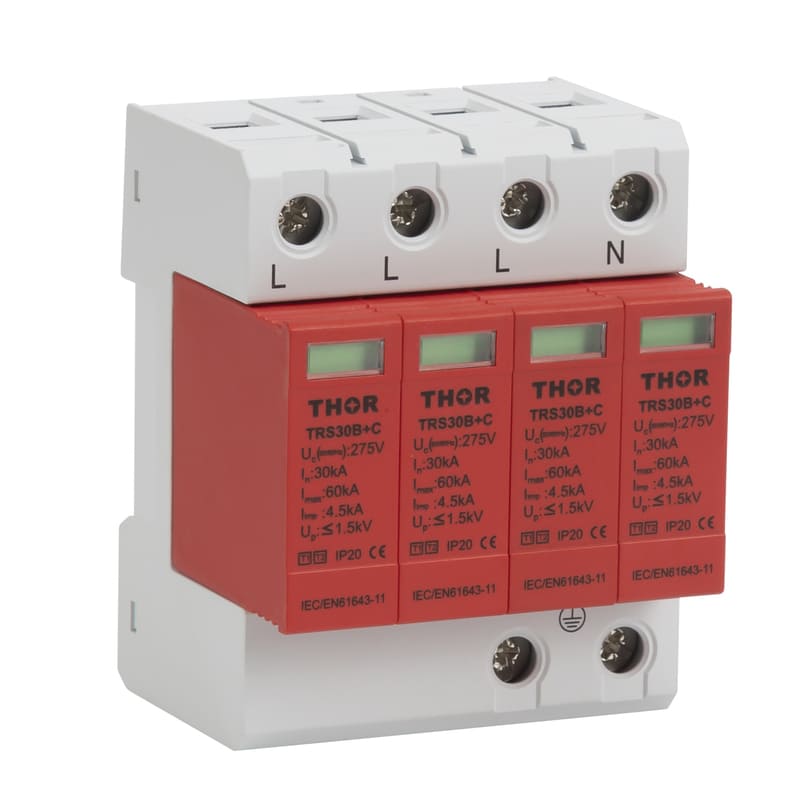
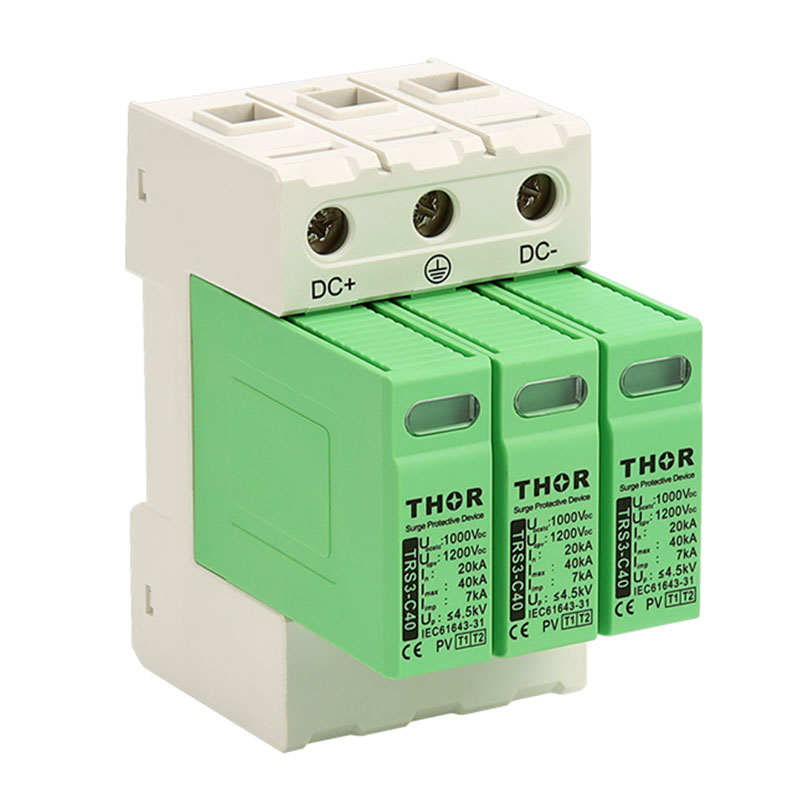
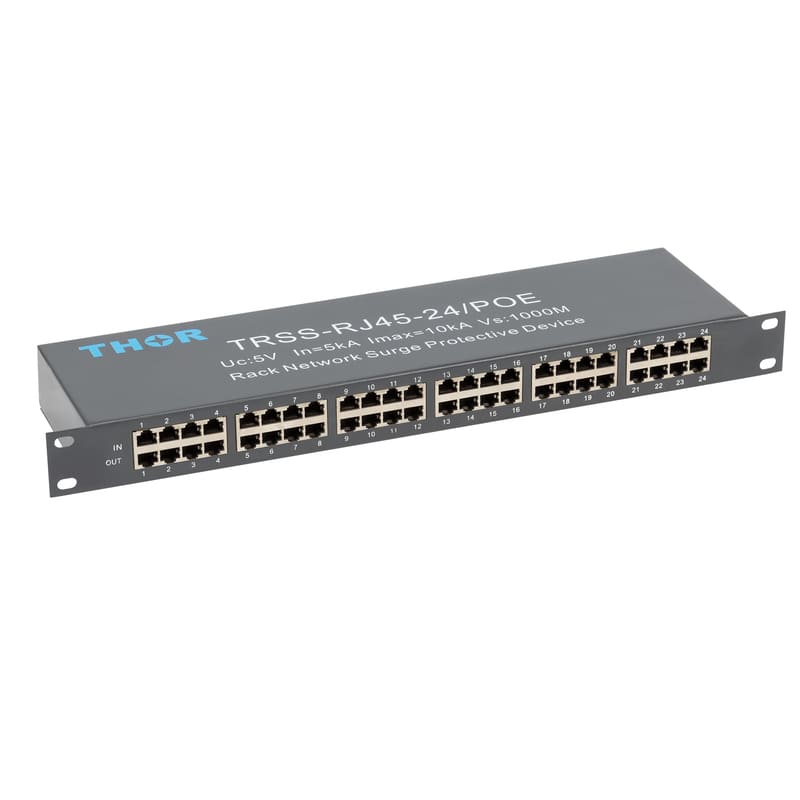
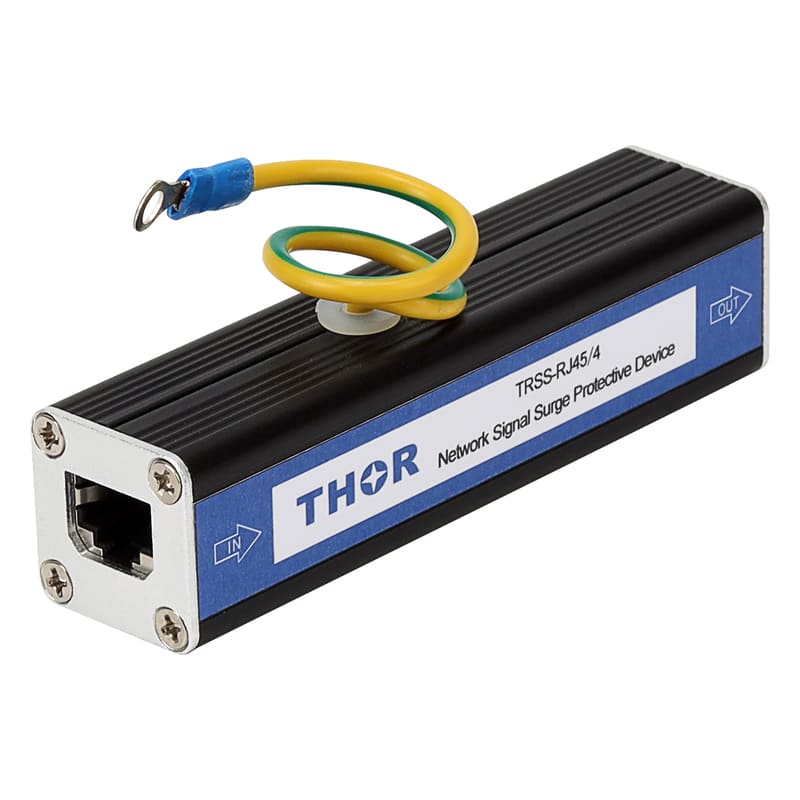
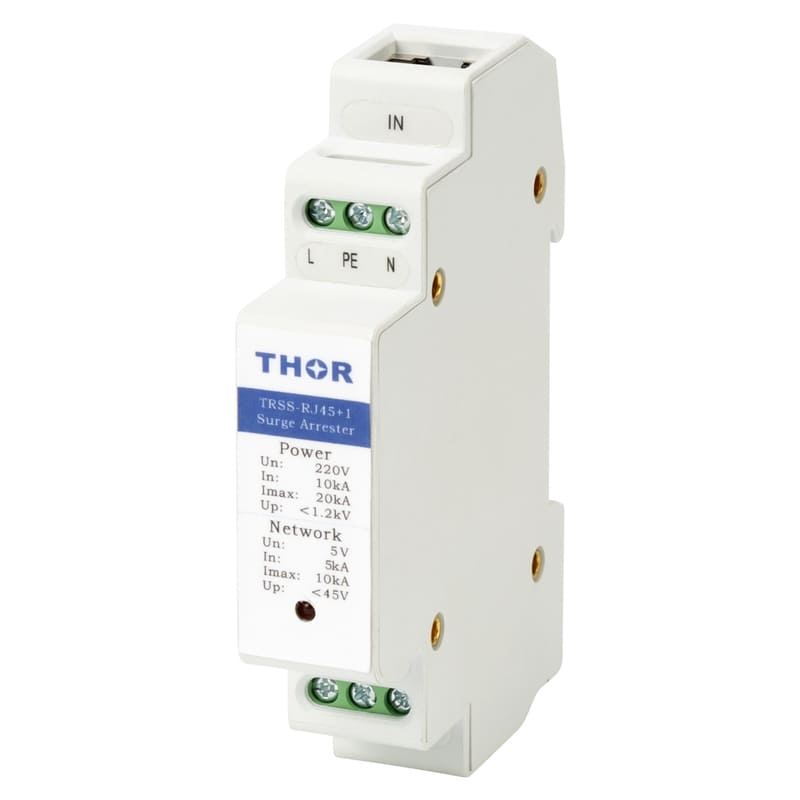
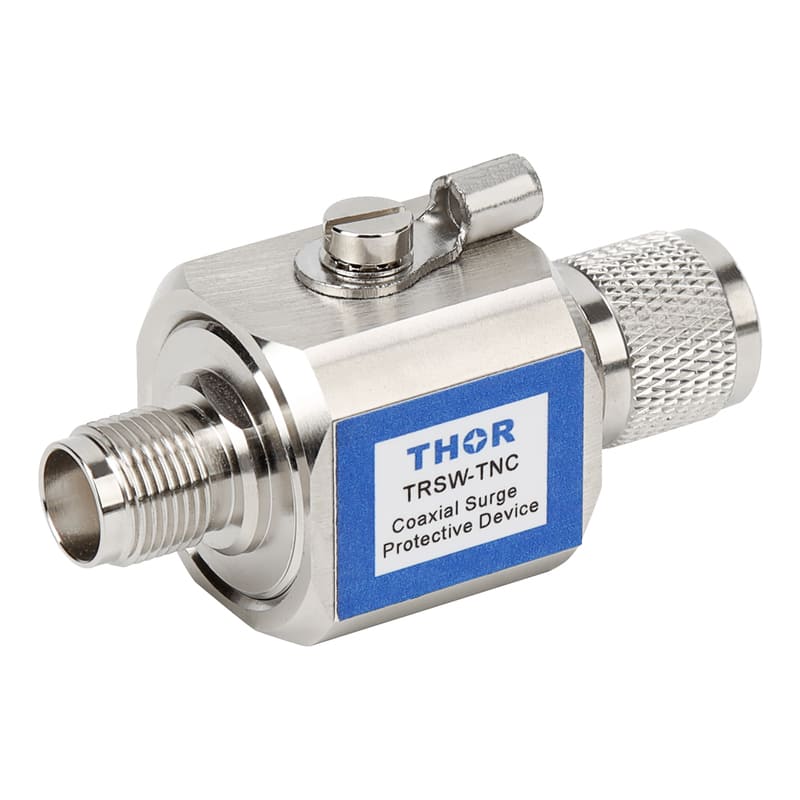
In order to reduce the impact of lightning on concrete buildings, a series of effective lightning protection measures need to be taken. These measures include installing a reliable lightning protection system, strengthening electrical grounding (surge protectors must be installed in electrical lines), and using lightning protection materials. At the same time, in thunderstorm weather, people should try to avoid outdoor activities or contact with items that may cause lightning hazards. For important concrete buildings and facilities, lightning protection detection and maintenance should also be carried out regularly to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of their lightning protection systems.
If the lightning current attacks concrete with steel bars, the situation will become relatively complicated because the presence of steel bars will change the conduction path and effect of the lightning current. The following is a detailed analysis of this situation:
1. Lightning current conduction path
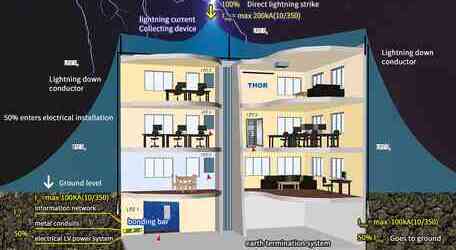
Rebar as a conductive channel: Rebar plays a skeleton role in concrete and also has good conductivity. When lightning current attacks the concrete surface, it is likely to be quickly conducted along the steel bars because the steel bars provide a low-impedance path. Lightning current will flow along the steel bars to the ground to find a suitable release channel, which may cause the soil and groundwater near the ground to be affected.
Insulating effect of cement ground: Although concrete itself is an insulating material, its insulation performance may be challenged in the face of the huge energy of lightning current. However, the cement layer still plays a certain obstructive role and slows down the propagation speed of lightning current.
2. Possible impact
Damage to steel bars and concrete: Lightning current generates a lot of heat when passing through steel bars, which may cause local melting or gasification of steel bars, and may also cause cracks or peeling of the cement layer. The melting or gasification of steel bars will weaken its structural strength, while the damage of the cement layer will affect the overall stability of the ground.
Electromagnetic radiation and shock waves: Lightning current will generate strong electromagnetic radiation and shock waves during the conduction process. These energies may interfere with or damage nearby electronic equipment, and may also cause harm to personnel.
Safety risks: If there are underground facilities (such as pipelines, cables, etc.) under the cement floor, the lightning current may be conducted to these facilities through the steel bars, causing accidents such as fires and explosions. In addition, if people happen to be in the nearby area when the lightning strikes, they may suffer injuries such as electric shock and burns.
III. Protective measures
Install lightning protection facilities: Install lightning protection facilities such as lightning rods and lightning strips around buildings or important facilities to guide the lightning current safely into the ground. Ensure that there is a good electrical connection between the lightning protection facilities and metal components such as steel bars so that the lightning current can be quickly conducted underground.
Strengthen electrical safety: Regularly inspect and maintain electrical equipment to ensure that it is in good condition. In thunderstorms, try to avoid using non-essential electrical equipment and turn off unnecessary power. Electrical equipment that must be turned on must be equipped with surge protectors to protect the lightning protection safety of the equipment.
Improve safety awareness: Strengthen the public's publicity and education on lightning protection knowledge and improve people's safety awareness. In thunderstorms, try to avoid outdoor activities, especially avoid staying in open areas or places such as tall trees and electric poles that are easy to become lightning targets.
In summary, when lightning current strikes a reinforced concrete surface, a series of complex effects and consequences may occur. Therefore, effective protective measures must be taken to ensure the safety of personnel and facilities.